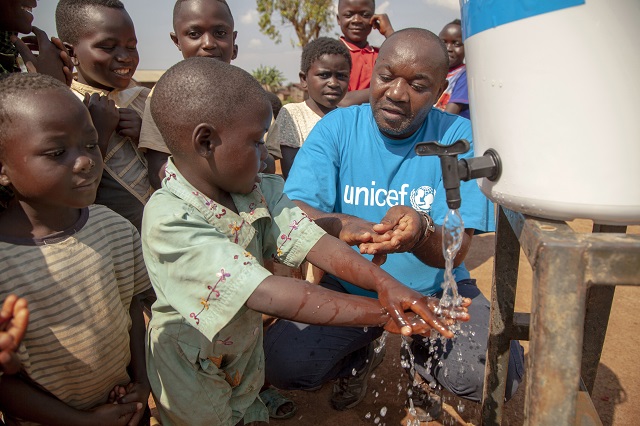

Since August last year the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has been facing its 10th Ebola virus disease outbreak. As of early March this year, 907 cases and 569 deaths have been reported.

If you use such social media websites as Facebook and Twitter, you may have come across posts flagged with warnings about misinformation. So far, most misinformation – flagged and unflagged – has been aimed at the general public.

Over the last two decades, industry funding for medical research has increased globally, while government and non-profit funding has decreased.

Since August last year the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has been facing its 10th Ebola virus disease outbreak. As of early March this year, 907 cases and 569 deaths have been reported.
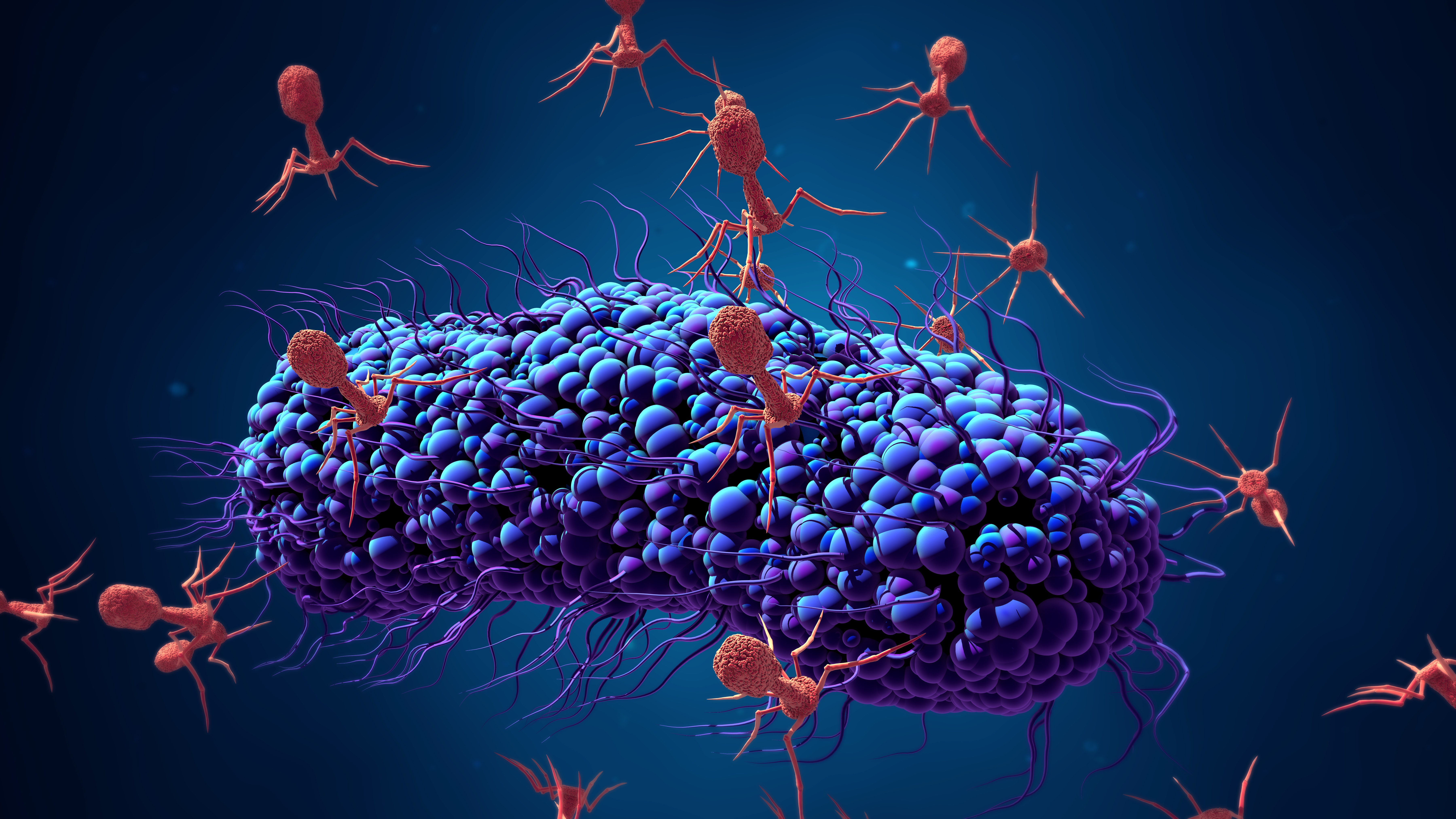
Antibiotics won the battle against resistant bacteria, but they may not win the war. You probably know that antibiotic-resistant bacteria, also known as superbugs, have hampered physicians’ ability to treat infections.
 Extra, extra! The embargo’s lifted, read all about it. Rumors were flying through the blogosphere this winter: physicists at the Advanced Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) may finally have directly detected gravitational waves, ripples in the fabric of space-time predicted by Einstein 100 years ago in his general theory of relativity. Gravitational waves were predicted to be produced by cataclysmic...
Extra, extra! The embargo’s lifted, read all about it. Rumors were flying through the blogosphere this winter: physicists at the Advanced Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) may finally have directly detected gravitational waves, ripples in the fabric of space-time predicted by Einstein 100 years ago in his general theory of relativity. Gravitational waves were predicted to be produced by cataclysmic...

Health is one of the biggest topics searched for on the web, yet despite its importance a large portion of this information is inaccurate, anecdotal or biased.
There is great enthusiasm for using “big data” to enable better biomedical research across the globe. But big data isn’t just about collating lots of old and new records. Including ongoing real-time data from patients can be part of a brave new world in health research.
Recognizing the difference between tumors and normal brain tissue during surgery is a major challenge. Removing healthy tissue can cause neurologic problems, but leaving tumor tissue behind can allow the cancer to spread again.
Nearly 13m more adults in the US will be eligible for statins after new guidelines widened the criteria for use of the drugs to treat high cholesterol and prevent heart attacks and strokes.
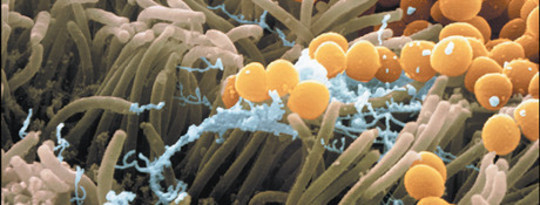
A genomic survey of the fungi living on our skin provides a framework for understanding how these microbes contribute to skin health and disease.
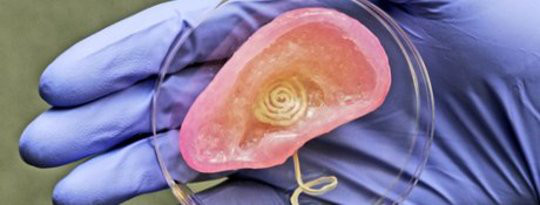
Researchers used 3-D printing to create functional bionic ears that receive radio signals. Using similar techniques, it may one day be possible to create bionic implants and prostheses....

A hormone called betatrophin prompts cells in the pancreas to multiply and produce more insulin. The finding, in mice, may lead to new ways to combat diabetes....

Scientists have created artificial kidneys that can filter blood and produce urine when transplanted into rats. With further development, this approach could help the many patients who await organ transplants because their own kidneys no longer work.
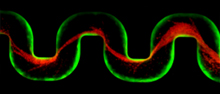
Bacterial communities called biofilms can quickly clog medical devices such as stents and catheters by forming 3-dimensional streamers that block flow. The finding will inform future approaches to prevent these deadly clogs....
A new study revealed the patterns of brain activity that produce human speech. This research may one day lead to new methods for treating speech disorders....
The flatworms that cause the tropical disease schistosomiasis can survive inside infected people for decades. The discovery of the stem cells that may be responsible could now lay the groundwork for new strategies to treat the disease....
Scientists successfully identified and grew a renewable population of liver stem cells for the first time, a new study reported. The findings could eventually lead to approaches that help rejuvenate damaged livers in people....
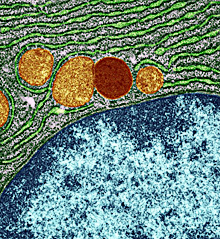 Scientists designed a compound that induces a cell "housekeeping" process that may help fight cancer, infection, neurodegenerative disease and aging. The compound successfully protected laboratory mice from deadly infections....
Scientists designed a compound that induces a cell "housekeeping" process that may help fight cancer, infection, neurodegenerative disease and aging. The compound successfully protected laboratory mice from deadly infections....

Preliminary study results suggest that a biomarker may be associated with the ability of young and middle-aged people to fight off a cold caused by a particular rhinovirus. The biological marker identified in the study was the length of telomeres—cap-like protein complexes at the ends of chromosomes—which shorten with age.
Scientists have identified a rare type of neuron in mice that's responsible for detecting the pleasant stroking of skin. The finding opens the door to exploring the molecules and neural pathways that recognize a positive touch....
Page 1 of 2

